Glass instrument and parhelia
Date
1700
Creator
Unknown, Engraver
Creator - Organisation
The Royal Society, Publisher
Object type
Article identifier
Material
Technique
Subject
Content object
Description
Figures from issue 262 of Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society.
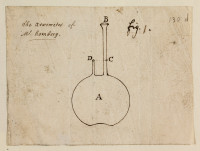
Figure I. A glass instrument, designed by Wilhelm Homberg and used to experiment on acidic spirits. Illustration to ‘III. Part of letter from Mr. Geoffrey, F. R. S. to Dr. Sloane, concerning the exact quantity of acid salts contained in acid spirits’ in Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, vol. 22, issue 262 (March 1700). Original proofs of this image can be found in MS/366/5/7 and MS/131/134-D.
Figure II. Diagram illustrating parhelia, or mock suns, as observed by Stephen Gray in Canterbury, England, February 1699. Illustration to ‘IV. Part of a letter from Mr. Gray, concerning an unusual parhelion and halo.’ in Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, vol. 22, issue 262 (March 1700). Original proof of this image can be found in MS/131/120-B.
Wilhelm Homberg (1652-1715), German natural philosopher, was not a Fellow of the Royal Society, and; Stephen Gray (c.1666-1736), British astronomer and dyer was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1733.
Figure I. A glass instrument, designed by Wilhelm Homberg and used to experiment on acidic spirits. Illustration to ‘III. Part of letter from Mr. Geoffrey, F. R. S. to Dr. Sloane, concerning the exact quantity of acid salts contained in acid spirits’ in Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, vol. 22, issue 262 (March 1700). Original proofs of this image can be found in MS/366/5/7 and MS/131/134-D.
Figure II. Diagram illustrating parhelia, or mock suns, as observed by Stephen Gray in Canterbury, England, February 1699. Illustration to ‘IV. Part of a letter from Mr. Gray, concerning an unusual parhelion and halo.’ in Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society, vol. 22, issue 262 (March 1700). Original proof of this image can be found in MS/131/120-B.
Wilhelm Homberg (1652-1715), German natural philosopher, was not a Fellow of the Royal Society, and; Stephen Gray (c.1666-1736), British astronomer and dyer was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1733.
Related fellows
Stephen Gray (1666 - 1736, British) , Astronomer
Associated place